
Tropical Rainforest
Rainforest Profile
The rainforest is a place that is thronging with life. Six percent of the world is covered in rainforests, and that percentage decreases every second. According to NatureNiche.com, there is a football field size of rainforest every second.
The rainforests around the world are located on the equator line. The heat and moisture is so intense, that life thrives in the harsh terrain. Thousands of plants and animals life in the rainforest, and many of the species there are only native to the rainforest.
Africa and south-east Asia have the most popular rainforests; however, South America has the mighty Amazon, which is a very large tropical rainforest.
The climate in the rainforest is hot and humid. An average rainforest gets 100-400 inches of rain a year. There are four layers to the rainforest: the emergent layer (the highest, lots of sunlight), the canopy (just below the emergent, good sunlight), understory (little sunlight, below canopy), and the forest floor (bottom layer, no sunlight). The soil is nutrient poor because the rain washes the nutrients away.
Environmental Threat
The rainforests are most commonly known in America by the people that stand for the preservation of them. People often say that deforestation will be the ruin of the jungles. With a football field of rainforest cut down every second, deforestation is probable environmental threat. The experts say that the release of carbon dioxide from the dead trees contributes to global warming. The massive amounts of carbon dioxide could be a result of global warming, but many other organisms create the same amount of CO2.
There are many different organizations world wide that contibute in the war against deforestation. Two thousand six hundred organizations exist wprld wide today that are supportive to the rainforest.
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is common in the rainforest, and most of the native animals interact with each other. An example of symbiosis is the relationship between the trees and the animals. Hundreds if not thousands of animals live in the trees or use them as shelter. That is an example of commenalism, for the tree is not affected, while the animals get a home.
Climate
The yearly average of percipatation and temperature is represented by this graph. Climate graphs.xlsx
Energy Transference
The chart below represents a part of the rainforest food chain. All levels are shown.
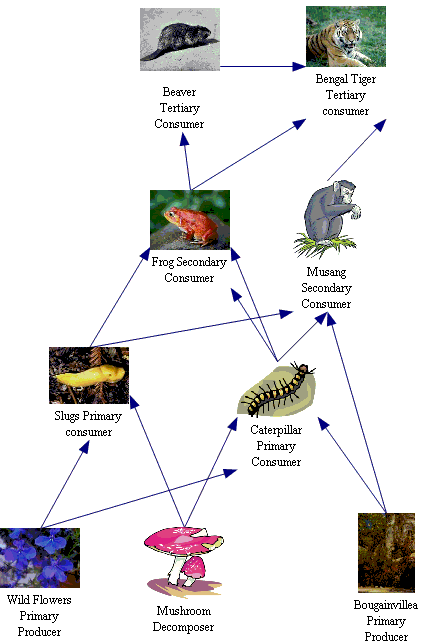
PLANTS
The Strangler Fig.
Ficus aurea., or the strangler fig, is a common tree species in the tropical rainforest. Its light bark, umbrella canopy, and buttressed roots are recognizable everywhere. They are adapted to live in their unique environment in a very unusual way. Beginning as epiphytes growing on a host tree, their roots and branches slowly wrap themselves around the host (strangling it) (parasitism) until it suffocates and dies, which is where it gets it name. This enables them to reach the much needed sunlight in the upper layers of the rainforest. Some strangler fig trees have flowers that can only be pollinated by a certain species of wasp, and in return, it gives them shelter, which is an example of (mutualism). Though the trees mentioned before can flower, other trees can only grow fruit. They are dropped on the ground to be eaten by animals who will disperse the seeds elsewhere. Native to Southeast Asia, strangler figs fruit are eaten worldwide.

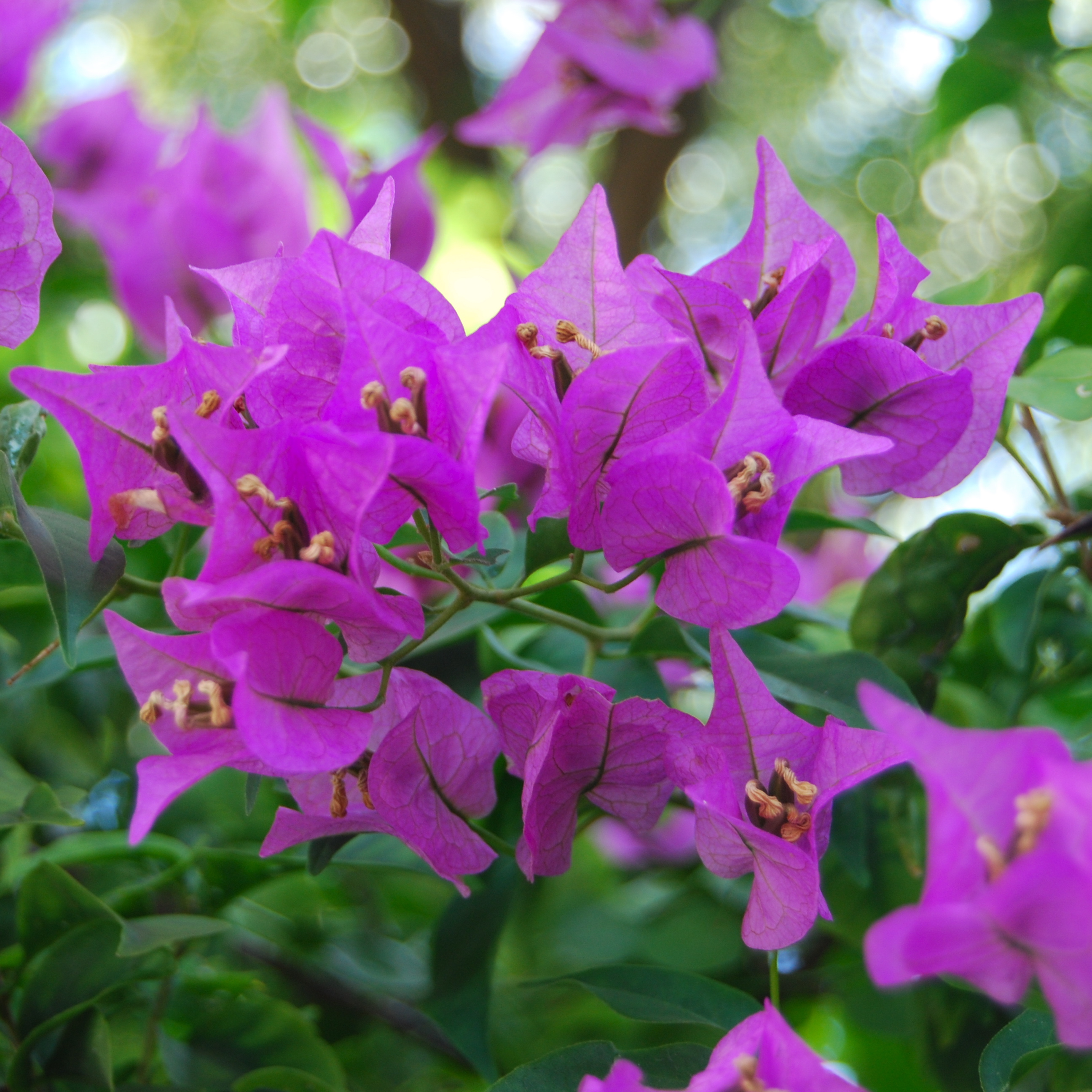
Bougainvillea:
Bougainvillea spectabilis, commonly known as a bougainvillea, is a beautiful flowering plant native to South America. With dark green leaves, and papery pink and red flowers, this plant can be a vine, shrub or tree, all very common in the rainforest. Well adapted to its home, bougainvilleas have hooks to cling on to other plants to hold them up, since their roots are very fragile, but the other planst are not affected. (commenalism) They can grow in sunshine or shade, and tend not to be affected by insects due to the presence of thorns. Some smaller bugs like aphids and larvae can find their way into them though. Drip tips on their leaves prevent excessive amount of water to pool in them.

Kapok Tree:
Ceiba pentandra of the class Magnoliopsida, also known as the Kapok Tree, is commonly found in tropical rainforests. These grey-barked, cylindrical trees are known for their large diameter of 9 feet. Branches on this tree grow in horizontal tiers and create an umbrella shape. The flowers that grow on this tree have an odor that attracts bats who pollinate them, but it is unpleasant for humans. When the trees are young, thorns are present to protect them from assorted animals. They are adapted to prevent infection by having the ability to heal broken limbs. Native to South America and West Africa, these trees are important to the rainforest environment. People of the rainforest use these trees to create canoes because of their buoyancy (parasitism).

ANIMALS
Bengal Tiger

Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Tigris
Species: Panthera
Common Name: Bengal Tiger
Physical Description: Orange/Brown skin, white cheeks, mouth, and stomach. It has long black stripes on it. The tiger can be up to 575 pounds. The fur of the tiger is very fine in texture.
Location: Found in most rainforests.
Behavior: Sneaky and quiet.
Nutrition: The Bengal Tiger is a carnivore. It eats boars, wild oxen, and other animals that live in the forest.
Reproduction: The Bengal Tiger mates any time of the year. It can have a litter of up to four cubs.
Adaptations: Orange Fur: Blends in with red and orange plants common in the rainforest, scratches at trees: to sharpen claws, Soft pads on bottom of feet: allows them to stalk prey silently.
Vital statistics: The average Bengal tiger can reach up to 575 pounds, ten feet long, and three feet tall.
Economic Importance: The Bengal helps regulate populations of their large herbivore prey.
Conservation: They are an endangered species.
Interesting Information: The tiger reaches full maturity at the age of five. The tigers' eyes, bones, and even whiskers are very valuable to researchers who are making medicine to treat or cure human ailment, and to give people a longer life.
| Black and orange stripes |
The colors help blend in the tiger. |
S |
| Long Claws |
The long claws are good for hunting their prey. |
S |
| Quiet and Sneaky |
They have soft paws on the bottom of their feet, this helps them to be quiet and sneaky
|
B |
| Carnivore |
They are carnivores because their body (long claws, and strong limbs) is meant to kill animals. |
B |
| Fine texture of fur |
The fine texture of fur helps the tiger be swift and fast. |
S |
Wagler's Pit Viper

Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Reptilia
Order: Squamata
Family: Viperidae
Genus: Tropidolaemus
Species: Wagleri
Common Name: Wagler's Pit Viper
Physical Description: The pit viper is a medium sized viper that can grow up to four feet in length. It is green, with a black border and many greenish crossbars on its back.
Habitat: The pit viper are mostly found in trees of the South East Asian Rainforest, but are still found in the majority of the rainforest's today. They live in trees, and grassy areas.
Location: Most of the pit vipers live in the South East Asian Rainforsest.
Behavior: The viper blends in with their evironment to hunt for food.
Nutrition: The Wagler's pit viper is a carnivore, and it mainly ests lizards, birds, and rodents.
Reproduction: Pit vipers are viviparous, which means that their babies are born live (no eggs). The eggs hatch inside of the mothers body.
Vital Statistics: The viper on average grows up to four feet in length, and it goes through four different phases until it reaches full majority.
Economic Importance: They are important because they are important in controlling to rodent populaion.
Conservation: The Wagler's pit viper is an endagered reptile.
Other intersting information: The pit viper can produce their own venom, and they can kill large animals more than twice their size. They are called Pit Vipers because they because they have pits just behind the nostrils which contain special organs that can sense heat and locate warm-blooded animals.
| Green Skin |
The snake can blend in with their envirnment. |
S |
|
Produces Venom
|
The snake produces venom to kill prey faster. |
P |
| Viviparous |
Babies are born inside of the mother. |
P |
| Carnivore |
Eats meat because there venom is made to kill animals. |
B |
|
Pits behind nostrils
|
The pits contain special organs that can sense heat and locate warm-blooded animals. This is an important adaptation since Wagler's pit viper is nocturnal and hunts at night. |
S |
Chimpanzee

Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Species: Troglodytes
Order: Primates
Family: Pongidae
Common name: Chimp
Physical Description: 3 to 5 feet tall anf they weigh around 99 to 176 pounds. They have black hait, and adults are often bald. All of their faces are hairless, and infants have pink faces that eventually become darker.
Habitat: They tend to sleep up in trees on branches.
Location: They are found in areas with numerous of tall trees mainly in the rainforest.
Behavior: Males hunt cooperatively for baby monkeys or bush pigs. Some groups have been observed to use thin ttwigs to extract termits form their nests.
Reproduction: Chimps are helpless are birth. After a few days the infant holds onto the mother's hair and at 5 to 7 months, it rides on her back. By four years the infant usually walks.
Nutrition: The favorite food of chimpanzees are fruits and young leaves, but they like many different types of food. In the dry season they will eat buds and blossoms, soft pitch, stems, galls, honey, bark and resin, seeds and nuts. Insects, like ants and termites are also in their diet. On rare occasions they will hunt small game like monkeys, pigs, and antelopes.
Vital Statistics: Chimps are on the endangered species list. There may be as many as 35,000 chimps in the wild, but destruction of their habitats, hunting and commercial trapping for the animal trade had reduced their population.
Conservation: Chimps are on the endangered species list. There may be as many as 35,000 chimps in the wild, but destruction of their habitats, hunting and commercial trapping for the animal trade had reduced their population.
Interesting Information: Chimps communities are made up of 15 to 100 members. Males tend to stay in the community that they are born into. Chimpanzess reach puberty at the age of seven. Females mature three to four years later then men. The average life span of a chimp is 60 years.
| Use thin twigs to keep termites away. |
This helps the chimps to stay in their habitat longer. |
B |
| Males hunt in groups. |
This helps them if they come across any threatening animals. |
B |
| Some chimps use wood to open up nuts. |
They use wood or stone tools as hammers to open up nuts to eat. |
B |
| Black hair |
This helps them hunt during the night. |
S |
| Strong fists |
They need strong fists to walk like they do (knuckle-walk). |
S |
Symbiosis: There are many symbiotic relationships that go on in the rainforest. An example of a symbiotic relationship is when a King Cobra eats another snake. A King Cobra mainly eats other snakes or other little mammals. The King Cobra benefits by getting its food and nutrients. The other snake gets harmed by getting killed by the cobra.
Citations:
http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/
http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/index.html
Josh is BLUE. I am in third period, what up? Hey fisher, this is Josh Drown, what a coincidence.
Jennifer is RED. I'm in fifth. Hahah yeah.
Austin is ORANGE.
Comments (17)
wikiuser0093 said
at 10:06 am on May 19, 2009
The animal person should work on the adaptations. jon p-4 :D
wikiuser0081 said
at 10:48 am on May 19, 2009
the animal person should work on the adaptations.
wikiuser0074 said
at 10:49 am on May 19, 2009
The chart at the very top of the page should be a bit bigger.
-Jessica P4 :)
wikiuser0105 said
at 11:31 am on May 19, 2009
I cant read the rainfall and percipitation charts, needs enlarged and need more exapmles of symbiotic relationships. Kelsey_P.5
wikiuser0016 said
at 11:39 am on May 19, 2009
The plant section is the best hahaha
Dante p.5
wikiuser0023 said
at 11:44 am on May 19, 2009
the graph at the top needs to be enlarged
Lexi p.5
Sara Sefcheck said
at 4:08 pm on May 19, 2009
check the mutualism example..
Sara Sefcheck said
at 4:09 pm on May 19, 2009
Like the format. Add more information to the environmental threat. What type of solutions?
Add some external hyperlinks to more information.
wikiuser0061 said
at 10:18 am on May 20, 2009
Animals have really good info and pictures... the best section i have ever seen in my whole life
Cody p.5
wikiuser0061 said
at 10:20 am on May 20, 2009
I meant Cody p.4
wikiuser0098 said
at 10:25 am on May 20, 2009
fish umm all i have too say is WOW!
your amazing!
wikiuser0123 said
at 4:14 pm on May 20, 2009
I really like the way you put a lot of information in all the categories. All of you who worked on it put all the information on it and it was neat and organized. I especially like the pictures.
wikiuser0123 said
at 4:15 pm on May 20, 2009
That last comment was me Kristy DePalo p.3
wikiuser0111 said
at 8:18 pm on May 20, 2009
you need to cite your sources.
animal info is great and detailed!
plant, you could put the headings so it's not just one paragraph.
Madi p.5
wikiuser0037 said
at 8:46 pm on May 20, 2009
It's really organized! :D Maybe you could use some charts for precipitation and temperature though?
Kayla P3
wikiuser0126 said
at 10:42 am on May 21, 2009
The animal info is good. The pictures are very detail and high quality so you can really get to see what the animals are like. Hunter G. P.5
wikiuser0006 said
at 4:55 pm on May 21, 2009
hey austin it's kai thanks for the help today :D your the best
You don't have permission to comment on this page.