Tropical Rainforests

General Information
Tropical rainforests are biomes with a warm, wet climate located near the equator (such as Central America, Indonesia, Malaysia, etc.). They have year round warmth, a wide variety of plant and animal life, and provide medicines and 40 percent of earth's oxygen. They consist of 4 parts or layers. One of the most well-known rainforests is the Amazon. Another specific rainforest is the Congolese.


Four Layers
The rainforest is made up of four layers; emergent trees, upper canopy, understory, and forest floor. Emergent trees are the highest up and spaced a good distance apart. The upper canopy gets most of the sunlight and makes it hard for everything below to get any. It is also where most of the animals live. The understory is made up of smaller trees and trunks of upper canopy trees. Lastly, the forest floor is usually shaded and doesn't contain very much plant life.
Climate
Tropical Rainforests rarely reach a temperature higher than 93 degrees farenheit or lower than 68 degrees farenheit. Because usually rains more than 100 centemeters a year, the average humidity is between 77 and 88 percent, but there is usually a brief season of less rain.
This graph shows the average monthly temperatures and precipitation. rainforest climate graph.xlsx
Life
Rainforests contain about 82 percent of the world's biodiversity ranging from reptiles, mammals, amphibians, etc. It has more kinds of trees than any other biome. Because of the thick canopy of trees, the forest floor does not have much life. Sunlight doesn't reach there. Because of the large amount of rainfall, the soil is not nutrient rich. Some specific things found in tropical rainforests are bamboo, coconut trees, stangler figs, chimpanzees, and jaguars.
There are also a lot of people that live in tropical rainforests like the Yanomamo tribe in the Amazon. The tribes get many of the things they use from the forest like clothes, food, and housing. The populatons of people living in rainforests is decreasing because of disease and deforestation.
Environmental Threat
An environmental issue in tropical rainforests is deforestation. Rainforests used to take up about 13 percent of earth's land surface. They now cover only 6 percent and continue to be destroyed at the rate of a half acre each second. Rainforests' value lie in all the wood we can get from them. This issue is important to address for many reasons. One is that rainforests hold nearly half of the world's plant and animal species. Cutting down their home may lead to extinction for some of them. Also, about 20 percent of earth's oxygen is produced just in the Amazon Rainforest. In addition, they give us foods, medicines, and materials that we use in everyday life.
There are many organizations working to conserve rainforests and inform people of the dangers if we were to lose them. Some are the Rainforest Action Network, APECA, Trees for the Future, and Mongo Bay. All these organizations are non-profit.
A good way to slow deforestation would be to stop using so much paper and other timber products. People can do every day things to help like using both sides of the paper and recycling. The other things we gain from rainforests are far to important to lose.

Symbiotic Relationships
Mutualism
-An example of mutualism is shown between ants and fungi. Ants cultivate the fungus and the fungus provides nutrients for the ants. Both organisms benefit from the relationship.
-Sloth hairs are grooved, and this allows algae to easily take hold and grow on the sloth's fur. This camoflauges the sloth and allows the algae to get closer to the sunlight.
Commensalism
-One way commensalism is shown in tropical rainforests is in bromeliads and frogs. Frogs get shelter and food from bromeliads while the bromeliad is unaffected. One organism benefits while the other is not affected.
Parasitism
-An exaple of parasitism is in strangler figs and trees. Strangler figs grow on the branches of trees. They begin to sprout roots that eventually go into the ground. The roots start to grow around the host tree and kill it. One organism benefits while the other is harmed.
Zoology
The rainforest consists of a very wide variety of animals. A lot of these animals are very brightly colored and are some of the most intriguing animals you will ever lay eyes on. The animals live in all of different parts of the rainforest, such as the forest floor and the canopy. You will find birds, fish, snakes, frogs, elephants, lions, and many other animals.
Bengal Tiger
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Panthera
Species: Tigris tigris
One of the animals found in the rainforest is the bengal tiger. Its scientific name is Panthera tigris tigris. The bengal tiger is found in Bangladesh, India, China, Siberia, and Indonesia. It has a distinctive reddish-orange coat with vertical black stripes. There are white spots above the eyes and behind the ears. The average life span of the bengal tiger is about eight to ten years, but when held in captivity, they can live up to 26 years. Their weight can be anywhere from 200 pounds to 930 pounds. The length can be from six and a half feet to twelve feet. Bengal tigers have the longest teeth of any cat; they are seven to ten centimeters in length.
Bengal tigers are mostly solitary and they are most active at night. These animals are carnivores, and their diet conists of boars, wild oxen, and monkeys. Bengal tigers do not associate with mates unless it is for reproduction. Their thick fur, soft pads, and the fact that they do not have a fear of water help them to be successful in the rainforest. Due to the fact that they are so high up in the food chain, they help regulate populations of other animals. The bengal tiger is an endangered species and there are efforts being made to help preserve this species.

King Cobra
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Reptilia
Order: Squamata
Family: Elapidae
Genus: Orphiophagus
Species: Hannah
The scientific name of the king cobra is Ophiophagus hannah. This animal is found in southeast Asia. You can find king cobras on the edges of the rainforest or near bamboo stands. King cobras can be yellow, green, brown, or black, although they are usually yellow or white with cross-bars. The average life span is about twenty years. A king cobra can weigh between twelve and twenty pounds, and its length can be from twelve feet to eighteen feet.
King cobras mate once a year and they lay about eighteen to fifty eggs. It takes these eggs 70-77 days to hatch. The king cobra is the only snake that builds a nests and stays around to guard its eggs. These animals are active by day. A king cobra's diet consists of other snkes, some lizards, frogs, and small mammals. When this animal feels threatened, it will form a hood. A king cobra can raise up to one-third of its length. Although this species is not endangered yet, it is definitey at risk.

Barred Fruiteater
Kingdom: Animalia
Order: Passeriformes
Family: Contingidae
Genus: Pipreola
Species: Arcuata
The barred fruiteater's scientific name is Pipreola arcuata. These magnificent birds are found in the northern Andes mountains. Barred fruiteaters have a black head and are olive green on the rest of their other upper body parts. There are large yellow spots on the inner wings. Barred fruiteaters have hook-tipped bills and bright scarlet legs. These birds can weigh from 3.9-4.5 ounces and have a length of 8.5-9 inches.
Barred fruiteaters are mostly solitary, and they survive off of fruit and insects. These birds have an unmistakable shrill call. Although barred fruieaters are uncommon, they are not considered endangered.

Plant Life-
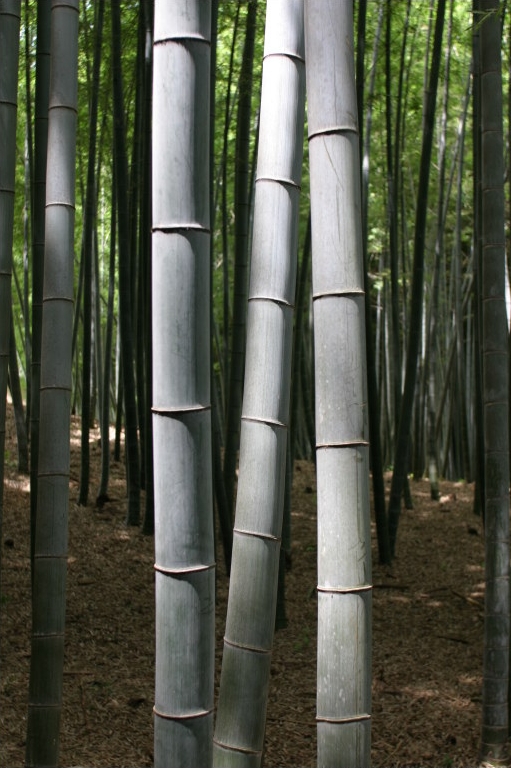

Bengal Bamboo-
Can be found in the biome of Southeast Asian rainforest. The common names are the Spinless Indian Bamboo or the Calcutta Cane. It grows best in a most enviroment with a lot of rainfall. It likes temperatures of about 40-90 degrees fahrenheit. This bamboo can grow between 40-80 Ft tall, and approximately 3 inches in diameter. The bamboo has dark green stems and the leaves are long and narrow. Bamboo is a perennial plant, it is not a shrub or tree, it is actually a grass. Bamboo grow to their full maturity by 3 months. Their typical lifespan is 25-40 years.
This certain bamboo is important to our enviroment because it can help to reduce soil erosion by sucking up the water caused by rain that might cause flooding. Bamboo is widely used for many other things besides just helping with soil; it is used for furniture making, making baskets, reinforcing concrete, fishing rods, and also to make a sacred flute called the "Eloo". While the Bengal bamboo is not an endangered species, rainforest are still decreasing by the minute and taking bamboo with it. Some people are trying to make the effort to help and conserve it in their homestead and forest areas by planting it and being aware of how much they hould harvest.
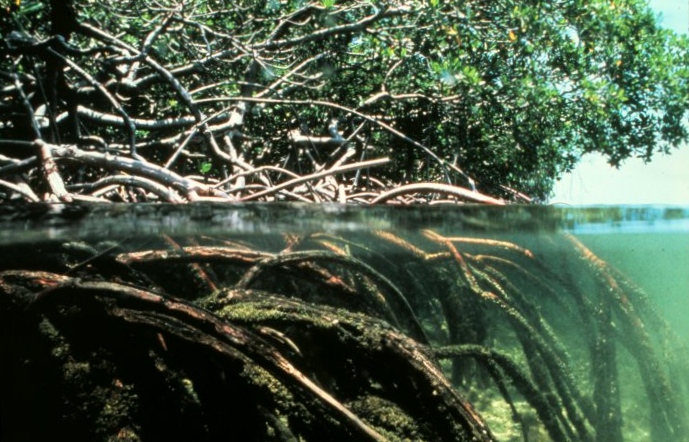

Mangrove Forest-
Mangroves are a special woody type of tree that lives along the edge, usually where the rainforest meets the ocean. They tend to grow in wet land places that other plants cannot grow.
They help protect the coastline by preventing erosion by collecting sediment as it flows. There are about 39.3 Million acres of Mangrove Forest all around the world, of that 39.3, 27% are found in Southeast Asia.

Strangler Figs-
Common name the Banyan Tree, is one of the most important plant species of the rainforest ecosystem. Hundreds of animals feed off of the sweet fruit produced by the fig tree. Figs bear friuts several times a year. In some forest up to 70% of its animals depend on fig in their diets. Fig trees are tall canopy trees that can grow to be a height of 148Ft.

Durian-
Commenly known as the Civet Fruit, can grow to heights of 90-130ft. Their trunks are straight and form about 4ft in diameter, the bark is dark brown and the branches can be straight or curved and covered in gray or coppery scales. Some of the adaptations are that the flowers have a strong color which attracts the Dawn Bat, its principle pollinator. The fruits also have hazardes, when the fruit is ripe there are 3-7 sided pointed spites. It also has a powerful odor, the smell of decaying onions.
It is believed that they only die when they are cut down or blown down in a storm, so they live for a long time. There are at least 15 different species of Durians , so they keep producing. They are mainly found in Southeast Asia, and are considered to be the most ancient and primative trees there. Unlike many other flowers, it replys on animals to disperse its seeds. It also bears large fruits directly from its trunk and main branches.
Example of Parasitism-
Monkeys carry ticks on their bodies and the ticks are a parasite, because they are feeding off the monkeys blood.
Cites-
Main site used: Blueplanetbiomes.org
Supplemental site used: MDG.net
Food Web
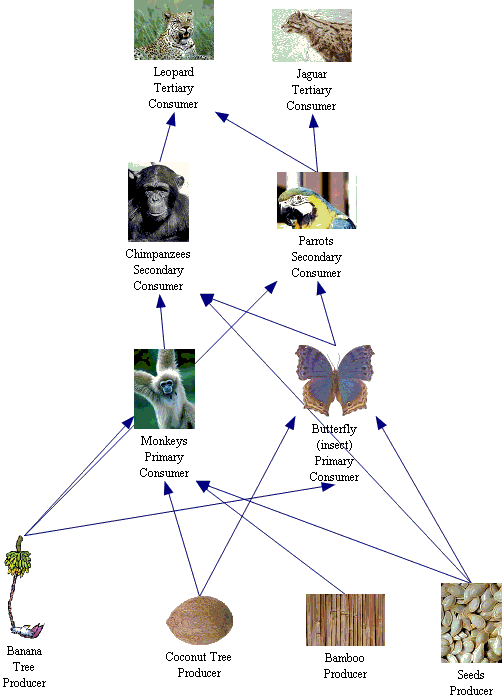
Citations
Mattison, Chris. Amphibians and Reptiles: Snakes. Danbury: Scholastic, Inc., 2005.
Pat, Morris. Mammals: Small Carnivores. Abingdon: Scholastic, Inc., 2003.
"Rainforest animals: Zoom Rainforests." Enchanted Learning. 20 May 2009
<http://www.enchanedlearning.com/subjects/rainforest/animals/rfbiomeanimals.shtml>.
"Rainforest Biomes." Blue Planet Biomes. 20 May 2009 <http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/rainforest.htm>.
"What's It Like Where You Live? MBGnet. 20 May 2009 <http://www.mbg.net/sets/rforest/index.htm>.
Jaime p3-general information, environmental threat, food web, symbiotic relationship
Amanda-Period 4-Zoology
Kelsey-P.5- Plants, symbiotic relationship
Comments (10)
wikiuser0065 said
at 10:36 am on May 19, 2009
the person who wrote in turqouise has great information ! :D
wikiuser0093 said
at 10:43 am on May 19, 2009
This page is very descriptive, especially the plant profielses:D jon-p.4
wikiuser0023 said
at 11:44 am on May 19, 2009
food web is very clear and easy to understand :)
lexi-p.5
wikiuser0053 said
at 4:04 pm on May 19, 2009
Geese I cannot seem to get my layout to look like that. The page is great and the information is legitimate. Josh P-5
Sara Sefcheck said
at 4:22 pm on May 19, 2009
Need more general info. I like the design and format. Symbiotic relationships?
Sara Sefcheck said
at 4:22 pm on May 19, 2009
The graph needs to be bigger.
wikiuser0075 said
at 6:50 pm on May 20, 2009
You have good examples of symbiotic relationships and the environmental threat is informative.The Barred Fruiteater animal profile is a little short on info...
But overall great job :)
-Kayla, period 4
wikiuser0059 said
at 10:16 am on May 21, 2009
i like the pics! very easy to understand! -Diana p.4
wikiuser0103 said
at 3:02 pm on May 25, 2009
Good information. Very descriptive and easy to understand
Autumn P3
wikiuser0103 said
at 3:12 pm on May 25, 2009
Good information. Very descriptive and easy to understand
Autumn P3
You don't have permission to comment on this page.